Top 10 Publications
Renelt S, Schult-Dietrich P, Baldauf HM, Stein S, Kann G, Bickel M, Kielland-Kaisen U, Bonig H, Marschalek R, Rieger MA, Dietrich U, Duerr R. HIV-1 Infection of Long-Lived Hematopoietic Precursors In Vitro and In Vivo. Cells. 11(19) (2022) https://doi: 10.3390/cells11192968.
Schelle L, Côrte-Real JV, Esteves PJ, Abrantes J, Baldauf HM. Functional cross-species conservation of guanylate-binding proteins in innate immunity. Medical Microbiology and Immunology. 13:1-12 (2022) https://doi: 10.1007/s00430-022-00736-7.
Côrte-Real JV, Baldauf HM, Melo-Ferreira J, Abrantes J, Esteves PJ. Evolution of Guanylate Binding Protein (GBP) Genes in Muroid Rodents (Muridae and Cricetidae) Reveals an Outstanding Pattern of Gain and Loss. Frontiers in Immunology. 13:752186 (2022) https://doi: 10.3389/fimmu.2022.752186.
Rothenburger T, Thomas D, Schreiber Y, Wratil PR, Pflantz T, Knecht K, Digianantonio K, Temple J, Schneider C, Baldauf HM, McLaughlin KM, Rothweiler F, Bilen B, Farmand S, Bojkova D, Costa R, Ferreirós N, Geisslinger G, Oellerich T, Xiong Y, Keppler OT, Wass MN, Michaelis M, Cinatl J Jr. Journal of Experimental and Clinical Cancer Research. 40(1):317 (2021) https://doi: 10.1186/s13046-021-02093-4.
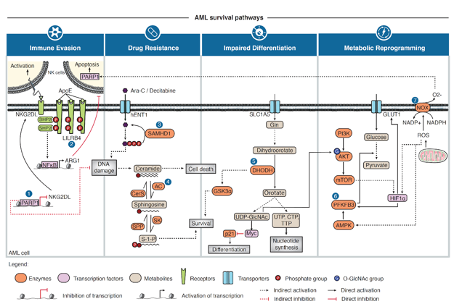
Nair R, Salinas-Illarena A, Baldauf HM. New strategies to treat AML: novel insights into AML survival pathways and combination therapies. Leukemia. 35(2):299-311 (2021) https://doi: 10.1038/s41375-020-01069-1.
de Sousa-Pereira P, Abrantes J, Bauernfried S, Pierini V, Esteves PJ, Keppler OT, Pizzato M, Hornung V, Fackler OT, Baldauf HM. The antiviral activity of rodent and lagomorph SERINC3 and SERINC5 is counteracted by known viral antagonists. Journal of General Virology. 100(2):278-88 (2019) https://doi: 10.1099/jgv.0.001201.
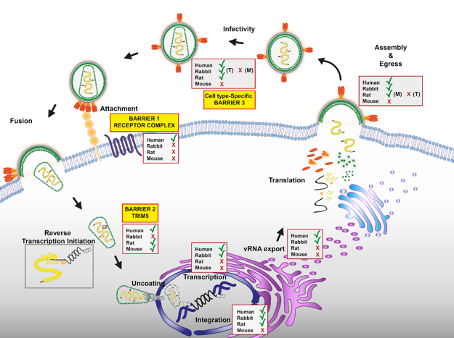
Baldauf HM, Stegmann L, Schwarz SM, Ambiel I, Trotard M, Martin M, et al. Vpx overcomes a SAMHD1-independent block to HIV reverse transcription that is specific to resting CD4 T cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences. 114(10):2729-34 (2017) https://doi: 10.1073/pnas.1613635114.
Schneider C, Oellerich T, Baldauf HM, Schwarz SM, Thomas D, Flick R, Bohnenberger H, Kaderali L, Stegmann L, Cremer A, Martin M, Lohmeyer J, Michaelis M, Hornung V, Schliemann C, Berdel WE, Hartmann W, Wardelmann E, Comoglio F, Hansmann ML, Yakunin AF, Geisslinger G, Ströbel P, Ferreirós N, Serve H, Keppler OT, Cinatl J Jr. SAMHD1 is a biomarker for cytarabine response and a therapeutic target in acute myeloid leukemia. Nature Medicine. 23(2):250-5 (2017) https://doi: 10.1038/nm.4255.
Baldauf HM, Pan X, Erikson E, Schmidt S, Daddacha W, Burggraf M, Schenkova K, Ambiel I, Wabnitz G, Gramberg T, Panitz S, Flory E, Landau NR, Sertel S, Rutsch F, Lasitschka F, Kim B, König R, Fackler OT, Keppler OT. SAMHD1 restricts HIV-1 infection in resting CD4(+) T cells. Nature Medicine. 18(11):1682-7 (2012) https://doi: 10.1038/nm.2964.
Tervo HM, Keppler OT. High natural permissivity of primary rabbit cells for HIV-1, with a virion infectivity defect in macrophages as the final replication barrier. Journal of Virology. 84(23):12300-14 (2010) https://doi: 10.1128/jvi.01607-10.